Blockchain technology has evolved beyond cryptocurrency, becoming a foundation for secure, transparent, and decentralized digital systems. From finance to healthcare, blockchain is driving innovation across various industries. In this guide, we explore the key uses of blockchain, how it works, and why it’s gaining global traction.
Understanding Blockchain Technology
What Is Blockchain?
Blockchain is a decentralized and distributed digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. Once a transaction is added to the blockchain, it becomes part of an immutable chain of records, which ensures transparency and security. The data is protected by cryptographic algorithms and consensus protocols, making it nearly impossible to alter retroactively.
How Blockchain Works
- Each block contains a list of verified transactions, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block.
- Once verified by network participants, the block is added to the chain.
- Altering a single block would require redoing all subsequent blocks and gaining control of 51% of the network—a nearly impossible task.
Core Applications of Blockchain
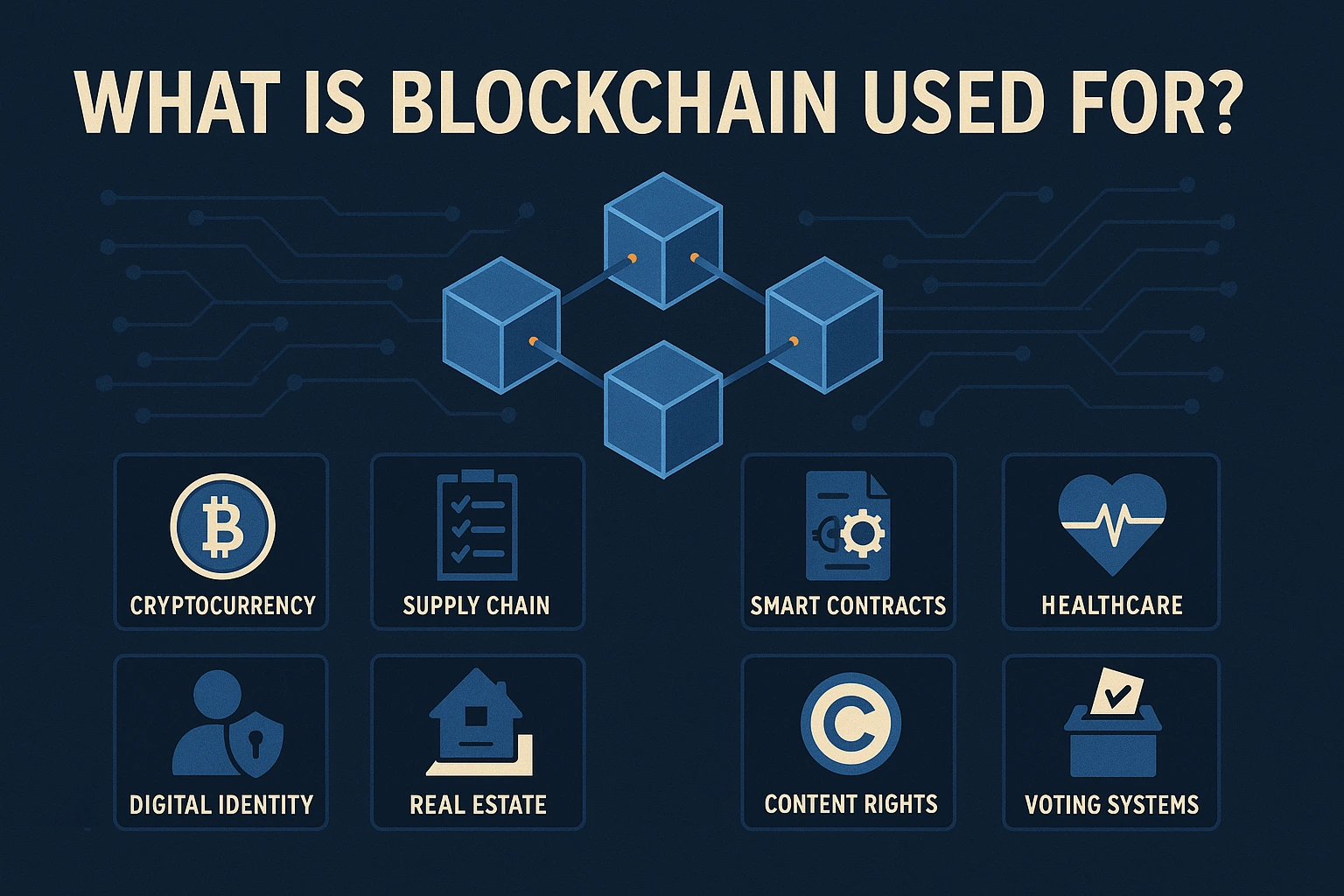
1. Cryptocurrency and Digital Payments
The most well-known application of blockchain is cryptocurrency. Bitcoin and Ethereum rely on blockchain to record transactions securely and transparently without a central authority.
2. Supply Chain and Logistics
Blockchain helps businesses track products from origin to consumer in real-time. It improves transparency, reduces fraud, and enhances trust in supply chain operations.
3. Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are self-executing programs on the blockchain that trigger actions when certain conditions are met. They automate processes such as payments, agreements, and settlements without intermediaries.
4. Healthcare
Blockchain secures patient data, supports interoperable health records, and helps reduce errors. It ensures privacy while allowing verified access across institutions.
5. Real Estate and Land Registry
Blockchain provides an immutable record of ownership for real estate, reducing fraud and simplifying property transfers. Smart contracts can also automate the buying/selling process.
6. Digital Identity
Blockchain enables users to create secure, verifiable digital identities that they can control. It eliminates the need for multiple logins and reduces identity theft risks.
7. Intellectual Property and Content Rights
Artists, musicians, and writers can protect their digital creations by recording copyrights and usage rights on blockchain. This helps ensure proper attribution and fair compensation.
8. Voting Systems
Blockchain-based voting ensures transparency and immutability, reducing the risk of tampering or voter fraud in elections. Voter identities can be verified without compromising privacy.
9. Insurance
Insurance companies use blockchain and smart contracts to streamline underwriting, policy issuance, and claims settlement—reducing administrative overhead and enhancing trust.
10. Energy Trading
Blockchain enables decentralized energy markets where individuals and companies can trade electricity securely and efficiently using smart contracts and real-time tracking.
Benefits of Blockchain Technology
- Transparency: Every transaction is recorded and viewable by network participants.
- Security: Cryptographic protection and decentralization reduce the risk of tampering.
- Immutability: Once recorded, data cannot be changed without network consensus.
- Efficiency: Automates manual processes and removes intermediaries.
- Traceability: Tracks the complete history of transactions or assets.
Limitations and Concerns
- Energy Consumption: Proof-of-Work blockchains require high energy input.
- Scalability: Some networks struggle with processing a high volume of transactions.
- Illegal Use: Anonymity can be misused for illicit transactions.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Legal frameworks vary by country and remain in development.
FAQs About Blockchain
What industries are using blockchain today?
Blockchain is used in finance, healthcare, logistics, energy, government, real estate, and the creative industries.
Is blockchain only used for cryptocurrency?
No. While it powers cryptocurrencies, blockchain is also used for smart contracts, supply chain tracking, identity management, and more.
Can data be edited or deleted from the blockchain?
No. Once a transaction is verified and added, it cannot be altered. This makes the data immutable.
Is blockchain secure?
Yes. Blockchain’s decentralized nature and cryptographic algorithms make it highly secure against fraud and tampering.
What is a 51% attack?
This refers to a scenario where a group gains control of over 50% of a blockchain’s network power, allowing them to alter transaction history. It’s extremely difficult and expensive to execute.
Conclusion
Blockchain is more than just the foundation of cryptocurrency. Its decentralized, transparent, and secure structure is transforming how industries operate. From digital payments to healthcare and beyond, blockchain is enabling more efficient, trustworthy, and innovative systems. As technology matures and regulations develop, its adoption is expected to grow exponentially across the globe.

Selina Davies is a technology writer and blockchain enthusiast with a passion for simplifying complex topics. With years of experience in fintech and decentralized systems, she focuses on educating readers about the future of digital innovation through clear, accurate, and engaging content.